POLYETHYLENE GUIDE

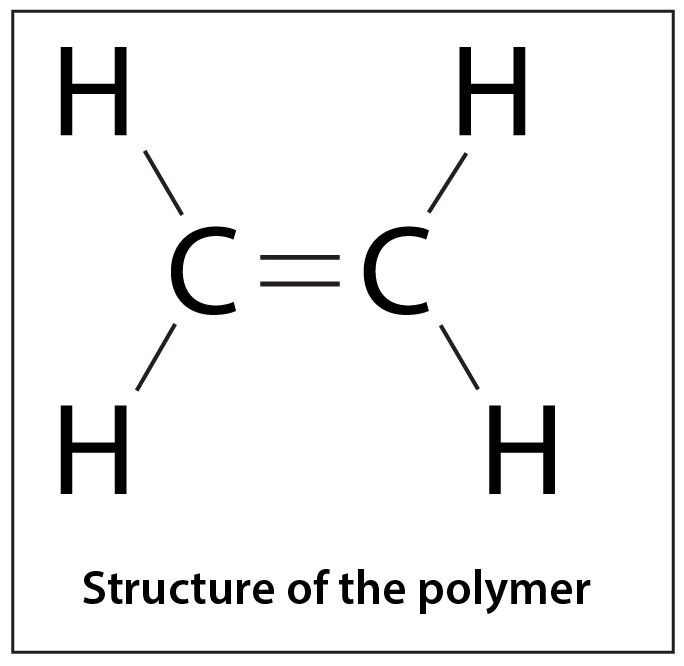
Polyethylene is a member of the polyolefin family alongside polypropylene. This group of materials is the most widely used, accounting for over half of thermoplastic consumption worldwide.
Properties
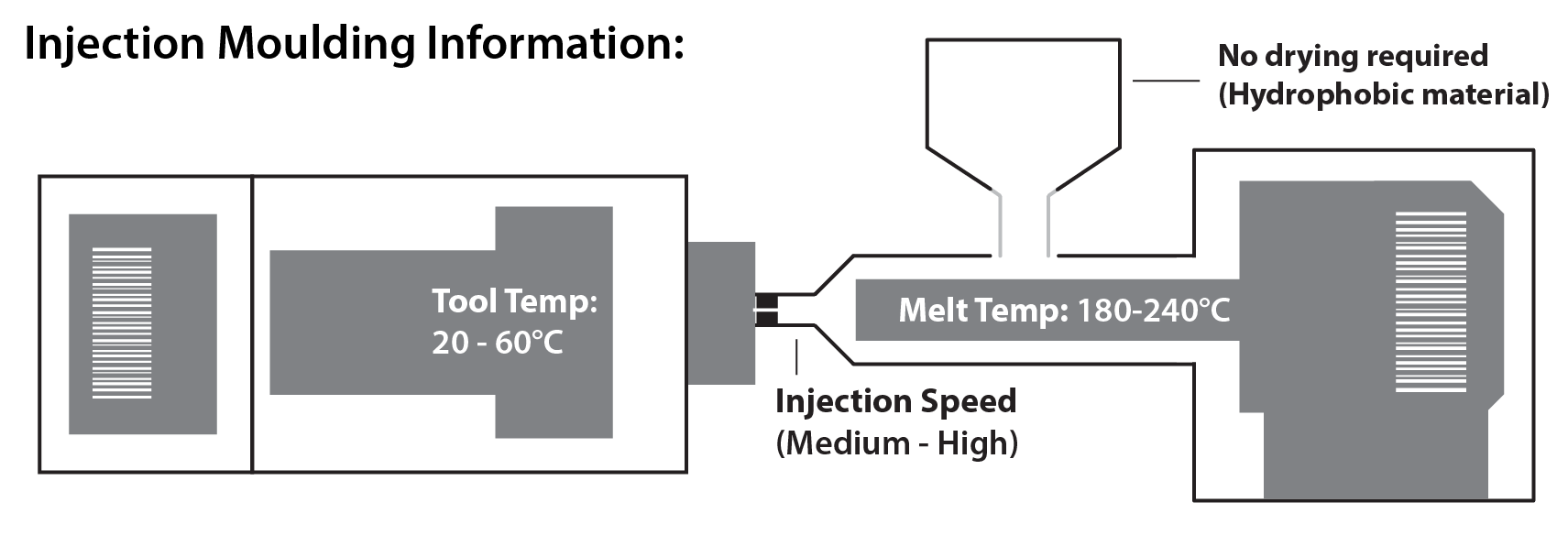
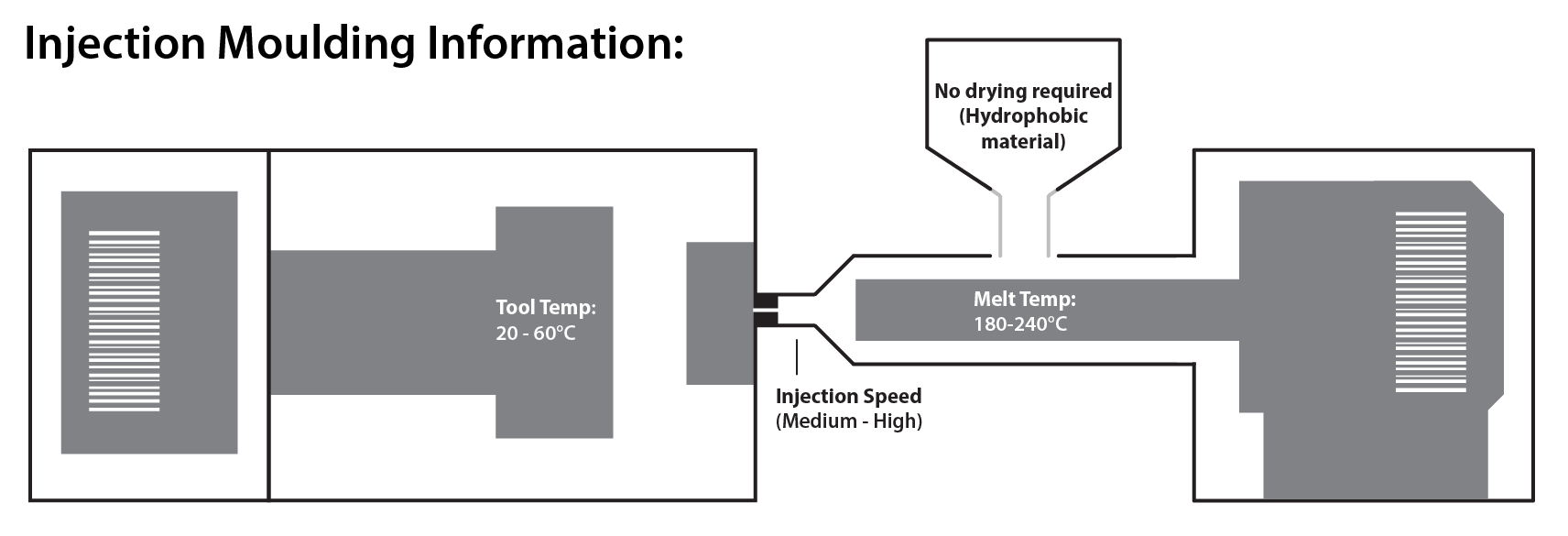
LLDPE was developed in the 1950s as a copolymer of polyethylene. It is made through a low pressure polymerisation process and is constructed of long linear polymer chains with a high number of short branches. These long linear polymer chains give LLDPE a high tensile strength, making it the preferred material in the manufacture of packaging films. LLDPE is commonly used in shopping bags and stretch wrap.
HDPE has greater hardness, rigidity, heat distortion temperature (HDT) and chemical resistance to LDPE, but a lower impact strength. It also has better low temperature properties than polypropylene homopolymer, however it is not as hard. Much like polypropylene, this material is resistant to boiling water and many corrosive chemicals.
Meanwhile, LDPE has only moderate tensile strength and still suffers from creep although it is tough. It does have excellent chemical resistance, impact resistance and insulation properties.
Finishing
Due to its waxy surface, polyethylene is not always suited to joining by using adhesives. Therefore, other methods of joining need to be considered, such as welding or snap-fits.
Additives
The properties of polyethylenes can be tailored by combining various additives. One of the most common examples of which is Antioxidants, which are used for process stabilisation. Alternatively, adding talc will enhance the mechanical properties of polyethylenes and improve their transparency.
Applications
Polyethylene is one of the most widely used plastics in the world. Including...